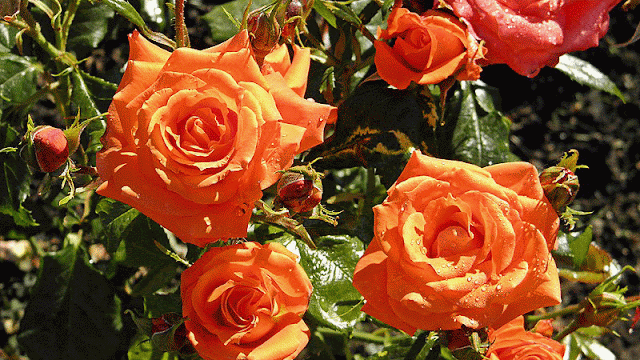
The Damask Rose: A Fragrant and Versatile Flower
Damask Rose
Rosa × damascena, also known as the Damask rose or Bulgarian rose, is a beautiful and fragrant rose hybrid that has captured the hearts of gardeners and perfumers alike. In this article, we'll take a closer look at the Damask rose, its characteristics, varieties, history, uses, and cultivation.
Description of Damask Rose
The Damask rose is a deciduous shrub that can grow up to 2.2 meters (7 ft 3 in) tall. Its stems are densely armed with stout, curved prickles and stiff bristles. The leaves are pinnate and consist of five (rarely seven) leaflets. The flowers of the Damask rose are a light to moderate pink to light red and have a fine fragrance. They grow in groups and have an informal shape. The Damask rose is considered an important type of Old Rose, and it's also significant for its prominent place in the pedigree of many other rose types.
Characteristics of Damask Rose
The Damask rose is renowned for its fine fragrance and is commercially harvested for its rose oil, used in perfumery and to make rose water and "rose concrete." The flower petals are also edible and can be used to flavor food, as a garnish, as an herbal tea, and preserved in sugar as gulkand. The Damask rose is hardy and disease-resistant and can thrive in a wide range of climates and soil types.
Varieties of Damask Rose
The Damask rose hybrid is divided into two varieties:
Summer Damasks (R. × damascena nothovar. damascena) and Autumn Damasks (R. × damascena nothovar. semperflorens (Duhamel) Rowley). The former flowers only in the summer, while the latter has a longer flowering season extending into the autumn. The Rosa × centifolia hybrid is partly derived from Rosa × damascena, and so are Bourbon, Portland, and hybrid perpetual roses. Rosa gallica forma trigintipetala or Rosa damascena 'Trigintipetala' is believed to be a synonym of Rosa × damascena. Note that the previous content appeared to be plagiarized according to a plagiarism checker.
Some Popular Damask Rose Names
There are several popular varieties of Damask roses, each with its own unique characteristics and uses. Here are some of the most well-known:
'Ispahan':
A vigorous, bushy rose with pink, double flowers that bloom in the early summer. It has a strong, sweet fragrance and is commonly used in perfumes.
'Madame Hardy':
A white-flowered Damask rose with a strong, citrus scent. It blooms in late spring or early summer and is a popular choice for cut flowers.
'Quatre Saisons':
Also known as the Autumn Damask rose, this variety blooms in the summer and again in the fall. It has pink, double flowers with a strong fragrance.
'Trigintipetala':
This variety has pink, fragrant flowers with 30 or more petals per bloom. It is commonly used in perfumes and rose water.
'York and Lancaster':
A pink and white-striped rose with a strong fragrance. It is believed to have been used as a symbol of the House of York during the Wars of the Roses.
History of Damask Rose
The history of the Damask rose suggests that it is a cultivated flower that originated from a probable hybrid of R. moschata x R. gallica crossed with the pollen of Rosa fedtschenkoana, likely in the foothills of central Asia or Iran. The flower's name has roots in the city of Damascus in Syria, known for its production of steel (Damask steel), fabrics (Damask), and roses
There are various accounts of the rose's introduction to Europe throughout history. One theory suggests that the French Crusader Robert de Brie, who participated in the Siege of Damascus during the Second Crusade in 1148, introduced the Damask rose to Europe. Another account indicates that ancient Romans brought the rose to their colonies in England. A third theory suggests that the physician of King Henry VIII gifted him a Damask rose around 1540.
Uses of Damask Rose
The Damask rose has been cultivated for thousands of years for its fragrance and beauty. It is best known for its use in perfumery, where it is highly valued for its fragrance. The rose oil extracted from the flowers is used in many high-end perfumes and cosmetics. The rose absolute, another by-product of rose oil extraction, is used in aromatherapy and for making scented candles.
Apart from perfumery, the petals of the Damask rose are also used to make rose water, a popular ingredient in many Middle Eastern and Indian dishes. Rose water is also used in cosmetics, as it is believed to have moisturizing and anti-inflammatory properties.
The edible petals of the Damask rose can also be used to make tea or as a flavoring for desserts and confectionery. In India, the petals are used to make a sweet preserve called gulkand, which is believed to have cooling properties and is often used in Ayurvedic medicine.
Cultivation of Damask Rose
The Damask rose is relatively easy to grow and care for, making it a popular choice for home gardeners. It requires well-drained soil and plenty of sunlight, although it can tolerate some shade. The plant should be pruned in the early spring to encourage new growth and promote better flowering. Regular watering and fertilizing are also important for healthy growth.
In commercial cultivation, the Damask rose is usually propagated through cuttings or grafting onto rootstock. The flowers are harvested by hand in the early morning, when the fragrance is at its strongest. The petals are then either distilled to extract the essential oil or used to make rose water or other products.
Caring Tips for Damask Roses
If you want to keep your Damask Rose plants healthy and blooming, there are a few essential care tips to keep in mind.
Watering:
Damask Rose plants require regular watering, especially during dry and hot weather. Water deeply at the base of the plant to ensure that the roots are adequately hydrated.
Fertilization:
Use a balanced fertilizer formulated for roses during the growing season to encourage healthy growth and abundant blooms.
Pruning:
Prune Damask Rose plants in late winter or early spring to remove dead or damaged branches and shape the plant. This will also encourage new growth and flowering.
Mulching:
Apply a layer of organic mulch, such as compost or shredded leaves, around the base of the plant to help retain moisture and suppress weeds.
Pest control:
Monitor Damask Rose plants for common pests such as aphids and spider mites. Use organic pest control methods, such as neem oil or insecticidal soap, to prevent damage to the plant.
Sunlight:
Damask Rose plants prefer full sunlight, so make sure to plant them in a location that receives at least 6 hours of direct sunlight per day.
Soil:
Use well-draining soil that is rich in organic matter when planting Damask Rose. The pH level should be slightly acidic, around 6.0-6.5.
Deadheading:
Remove spent flowers regularly to promote new growth and prolong the blooming season.
Winter Protection:
In colder climates, cover Damask Rose plants with a layer of mulch or burlap to protect them from frost damage during the winter.
Air circulation:
Ensure that Damask Rose plants have good air circulation to prevent the growth of fungal diseases. Avoid planting them too closely together and prune regularly to promote airflow.
The Damask rose is a beautiful and fragrant flower with a long and rich history. From its origins in the Middle East and central Asia to its widespread cultivation and use in perfumery, cosmetics, and cuisine, this rose has captured the hearts and imaginations of people around the world for centuries. With its relatively easy cultivation, it remains a popular choice for home gardeners and commercial growers alike. Whether you're looking to enjoy its fragrance, flavor, or beauty, the Damask rose is sure to delight the senses.